内脏脂肪:健康风险及其降低方法
内脏脂肪——围绕器官的危险腹部脂肪——会显著增加疾病风险。学习7条基于证据的策略,以降低内脏脂肪并改善代谢健康。
什么是内脏脂肪?
内脏脂肪是存储在腹腔深处、围绕肝脏、胰腺和肠道等重要器官的代谢活性脂肪组织。与皮下脂肪(皮肤下的脂肪)不同,内脏脂肪具有很高的炎性和代谢风险。
关键差异:内脏脂肪与皮下脂肪
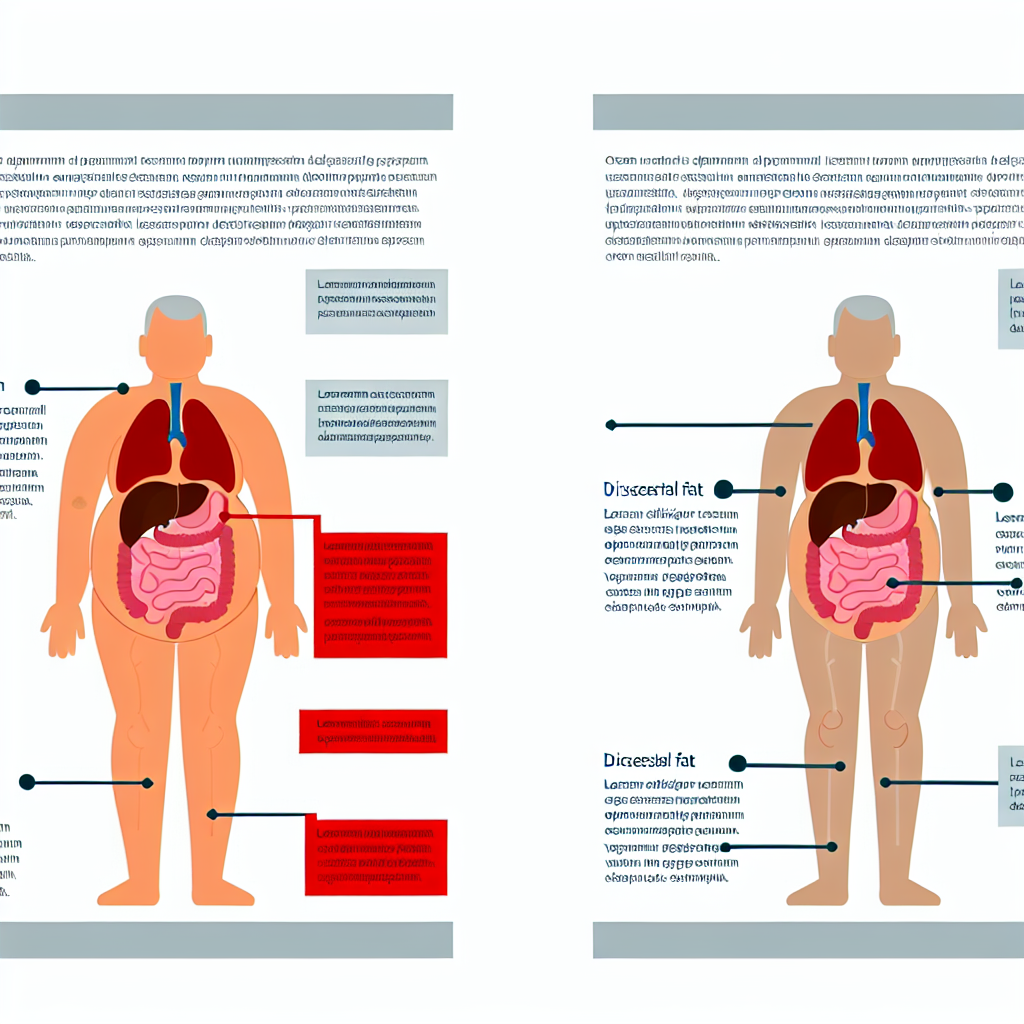
- • 在腹部深处,环绕器官
- • 高度新陈代谢活跃
- • 释放炎性细胞因子
- • 显著增加疾病风险
- • 在减重过程中首先减少
- • 皮下,易被捏出
- • 相对代谢惰性
- • 能量储存功能
- • 健康风险较低
- • 在减重过程中后减
为什么内脏脂肪危险
- 炎性信号传导:释放 IL-6、TNF-α 等细胞因子,驱动全身炎症
- 脂肪酸释放:直接进入门静脉,影响肝脏代谢并导致胰岛素抵抗
- 激素干扰:改变脂联素、瘦素及其他代谢激素
- 器官压迫:对周边器官造成物理压迫,影响功能
内脏脂肪的健康风险
即使 BMI 处于正常范围,内脏脂肪积累仍与多种慢性疾病独立相关:
Framingham Heart Study: Each 1cm increase in waist circumference = 1% higher cardiovascular risk
Meta-analysis: Visceral fat area >100 cm² associated with 4.3x diabetes risk (95% CI: 3.2-5.8)
AHA/NHLBI criteria: Waist >40" men / >35" women = primary metabolic syndrome criterion
Pooled analysis: High visceral fat linked to 20-60% higher risk for colorectal, breast, pancreatic cancers
如何测量内脏脂肪
存在多种评估内脏脂肪的方法,从家庭简单测量到高级影像成像:
Risk Cutoffs:
High risk: Men >40" (102cm), Women >35" (88cm)
Risk Cutoffs:
High risk: Men >0.90, Women >0.85
Risk Cutoffs:
Android/gynoid ratio, visceral fat area measurements
Risk Cutoffs:
>100 cm² at L4-L5 = high risk
7 条基于证据的内脏脂肪降低策略
这些策略专门针对内脏脂肪,并有同行评审研究记录的降低效果:
- 1.Create 500-750 calorie daily deficit (lose 1-1.5 lbs/week)
- 2.Visceral fat preferentially lost in early weight loss (before subcutaneous)
- 3.Track intake with food diary or app for accuracy
- 4.Focus on sustainable deficit, not extreme restriction
- 1.Target 1.6-2.2g protein per kg body weight daily
- 2.Include protein at every meal (25-40g per meal)
- 3.Lean sources: chicken, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt, legumes
- 4.Protein increases satiety and preserves muscle during weight loss
- 1.Resistance training: 3x/week, full-body, 70-80% 1RM
- 2.Cardio: 150-300 min/week moderate OR 75-150 min vigorous
- 3.Combined training superior to either alone for visceral fat
- 4.HIIT particularly effective: 3x/week, 20-30 min sessions
- 1.Extra virgin olive oil as primary fat (3-4 Tbsp daily)
- 2.Fatty fish 2-3x weekly (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- 3.Daily vegetables (5+ servings), fruits (2-3 servings)
- 4.Whole grains, legumes, nuts; limit red meat and processed foods
- 1.Remove sugar-sweetened beverages (largest source)
- 2.Eliminate processed snacks, baked goods, candy
- 3.Replace refined grains with whole grains
- 4.Read labels: avoid high-fructose corn syrup, added sugars
- 1.Consistent 7-8 hour sleep schedule
- 2.Sleep regularity as important as duration
- 3.Address sleep disorders (sleep apnea common with visceral obesity)
- 4.Improve sleep hygiene: dark, cool room, regular timing
- 1.Daily stress reduction: meditation, yoga, breathing exercises
- 2.Regular physical activity (doubles as cortisol control)
- 3.Adequate sleep (cortisol dysregulation with poor sleep)
- 4.Social connection and support systems
基于证据的内脏脂肪补充剂
这些补充剂在与饮食和运动结合时,有研究支持可降低内脏脂肪:
证据:
Reduces visceral fat via anti-inflammatory effects and improved insulin sensitivity
安全性:
Excellent - consult physician if >3g/day or on blood thinners
证据:
Meta-analysis: 1.3kg greater visceral fat loss when combined with exercise
安全性:
Good - monitor liver function with high doses, take with food
证据:
Improves insulin sensitivity, reduces visceral fat through AMPK activation
安全性:
Good - may cause GI upset initially, avoid if pregnant
补充剂只是辅助,不能替代饮食与运动。开始使用前请始终咨询医疗保健提供者。市场质量参差不齐——请选择第三方检测的产品(USP、NSF、ConsumerLab)。
常见问题解答
可以——这被称为“代谢性肥胖的正常体重”(MONW)或“瘦胖型”。约30%的正常 BMI 人群也存在内脏脂肪过量及相关的代谢功能障碍。腰围测量和身体成分测试比仅靠 BMI 更重要。
内脏脂肪对干预反应较快,减重初期比皮下脂肪更快。通过持续的饮食和运动,在5-10%体重下降后8-12周内,预计内脏脂肪降低25-40%。早期的体重下降优先针对内脏脂肪。
抗阻训练与有氧运动相结合最有效。Meta分析显示,抗阻 + 有氧训练使内脏脂肪降低约6.1%(SMD = -0.35)。HIIT(高强度间歇训练)尤为高效:每周3次、每次20-30分钟即可显著降低内脏脂肪。
不行——局部瘦身是一个迷思。然而,在减重过程中,内脏脂肪往往比皮下脂肪优先动员。不能直接针对内脏脂肪,但热量赤字+运动会先减少它。
遗传因素确实影响内脏脂肪的积累(约30-60% 为遗传性),但生活方式因素依然占主导。即使具有遗传易感性,饮食、运动、睡眠和压力管理也能有效降低内脏脂肪。基因可能设定底线,生活方式决定结果。
要点总结
内脏脂肪是代谢性最危险的脂肪组织,显著增加心血管疾病(2-3倍)、2型糖尿病(3-5倍)、代谢综合征(5-6倍)以及癌症(20-60%)的风险。好消息是:内脏脂肪对生活方式干预反应迅速。
- 热量赤字(每天 500-750 卡路里)在5-10%体重下降时可实现25-40% 的内脏脂肪降低
- 抗阻训练 + 有氧训练的组合是最有效的(约减少6.1%,SMD -0.35)
- 高蛋白饮食(占总热量的25-30%)较标准蛋白饮食更能提升内脏脂肪减少
- 地中海饮食配橄榄油比低脂饮食更能降低腰围
- 去除添加糖,尤其是含糖饮料(每天摄入将使内脏脂肪每年增加0.65 cm²)
内脏脂肪在减重的早期阶段更易减少——在皮下脂肪之前。这意味着即使体重仅有适度下降(5-10%),也会带来不成比例的代谢收益。请每月跟踪腰围;考虑使用 DEXA 扫描以客观量化进展。
